How To We Reach Our Goal
利用Matlab去進行 SIN 和 COS 之波型的模擬並採樣,其中的數值將全部轉換成0與1,之後將結果錄進去.txt 檔之中。 主要流程為:
可以參考以下圖片與程式碼:
sin波:
% Set parameters
f1 = 5000; % waveform frequency
fs = 32 * f1; % sampling frequency, ensuring 32 points per cycle
N = 12; % number of quantization bits
num_cycles = 2000; % number of cycles
samples_per_cycle = 32; % sampling points per cycle
% Generate time vector
t = 0:1/fs:(samples_per_cycle * num_cycles - 1)/fs;
% Generate sine wave
sin_wave = 2047 * sin(2 * pi * f1 * t);
% Quantize to 12 bits
quantized_wave = round(sin_wave);
% Convert positive and negative values to 12-bit signed values
% Set values greater than or equal to 2048 to the maximum value
quantized_wave(quantized_wave >= 2048) = 2047;
% Set values less than or equal to -2048 to the minimum value
quantized_wave(quantized_wave <= -2048) = -2048;
% Convert to 12-bit binary strings
binary_wave = dec2bin(quantized_wave + 2048, N);
% Write to text file
fid = fopen('C:\homework\Communication experiment\project\testdata_sin', 'w');
for i = 1:length(binary_wave)
fprintf(fid, '%s\n', binary_wave(i, :));
end
fclose(fid);
cos波:
% Set parameters
f1 = 5000; % waveform frequency
fs = 32 * f1; % sampling frequency, ensuring 32 points per cycle
N = 12; % number of quantization bits
num_cycles = 2000; % number of cycles
samples_per_cycle = 32; % sampling points per cycle
% Generate time vector
t = 0:1/fs:(samples_per_cycle * num_cycles - 1)/fs;
% Generate cos wave
cos_wave = 2047 * cos(2 * pi * f1 * t);
% Quantize to 12 bits
quantized_wave = round(cos_wave);
% Convert positive and negative values to 12-bit signed values
% Set values greater than or equal to 2048 to the maximum value
quantized_wave(quantized_wave >= 2048) = 2047;
% Set values less than or equal to -2048 to the minimum value
quantized_wave(quantized_wave <= -2048) = -2048;
% Convert to 12-bit binary strings
binary_wave = dec2bin(quantized_wave + 2048, N);
% Write to text file
fid = fopen('C:\homework\Communication experiment\project\testdata_cos', 'w');
for i = 1:length(binary_wave)
fprintf(fid, '%s\n', binary_wave(i, :));
end
fclose(fid);

波形之二進字
利用Verilog撰寫PSK的模塊,可以分成兩部分,分別為調變與解調:
程式碼如下:
// PSK Modulation
always @(posedge clk_1M or negedge rst) begin
if (!rst) begin
Mod_out0 <= 0;
Mod_out1 <= 0;
end else begin
if (M_out == 1'b0)
Mod_out0 <= cos0;
else
Mod_out1 <= sin1;
end
end
程式碼如下:
// PSK Demodulation
always @(posedge clk_1M or negedge rst) begin
if (!rst)
demod_out <= 0;
else if (received_signal == cos0)
demod_out <= 1'b0;
else if (received_signal == sin1)
demod_out <= 1'b1;
end
用於生成相位增量。每個時鐘週期增加固定的相位增量,輸出作為查找表的地址。
利用M-ary產生器,所產生的信號,可以分成兩個部分。
第一部分為clk_div,其通過計數來實現時鐘分頻,當計數達到設定的最大值 Max 時,
輸出時鐘信號 clk_div 翻轉一次。
這樣,輸出時鐘的頻率會是輸入時鐘的頻率除以 (Max+1)。
程式碼如下:
clk_div #(
.Max (500) // 設定參數 Max 的值為 500
) u3 (
.clk(clk), // 輸入時鐘信號
.rst(rst), // 輸入重置信號
.clk_div(clk_M) // 輸出分頻後的時鐘信號
);
第二部分為M_gen 模塊,其是一個多相序列生成器,通常用於生成偽隨機序列。
這些序列在數字通信、加密和測試中廣泛應用。
M 序列(Maximum Length Sequence)是由線性反饋移位寄存器 (LFSR) 生成的,
具有最大周期性且擁有良好的統計特性。
程式碼如下:
M_gen #(
.width (8) // 設定參數 width 的值為 8
) u4 (
.clk(clk_M), // 輸入分頻後的時鐘信號
.rst(rst), // 輸入重置信號
.M_out(M_out) // 輸出 M 序列信號
);
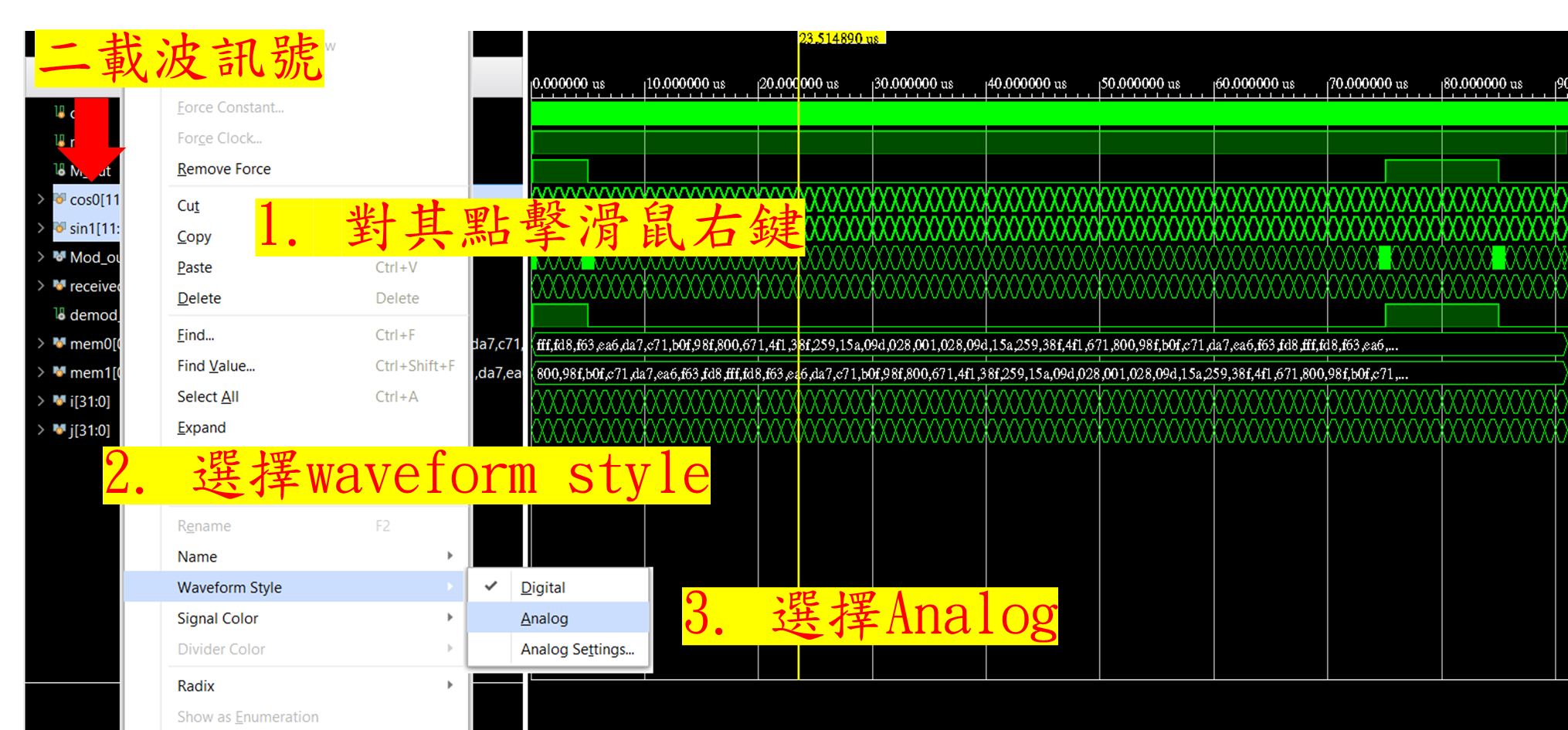
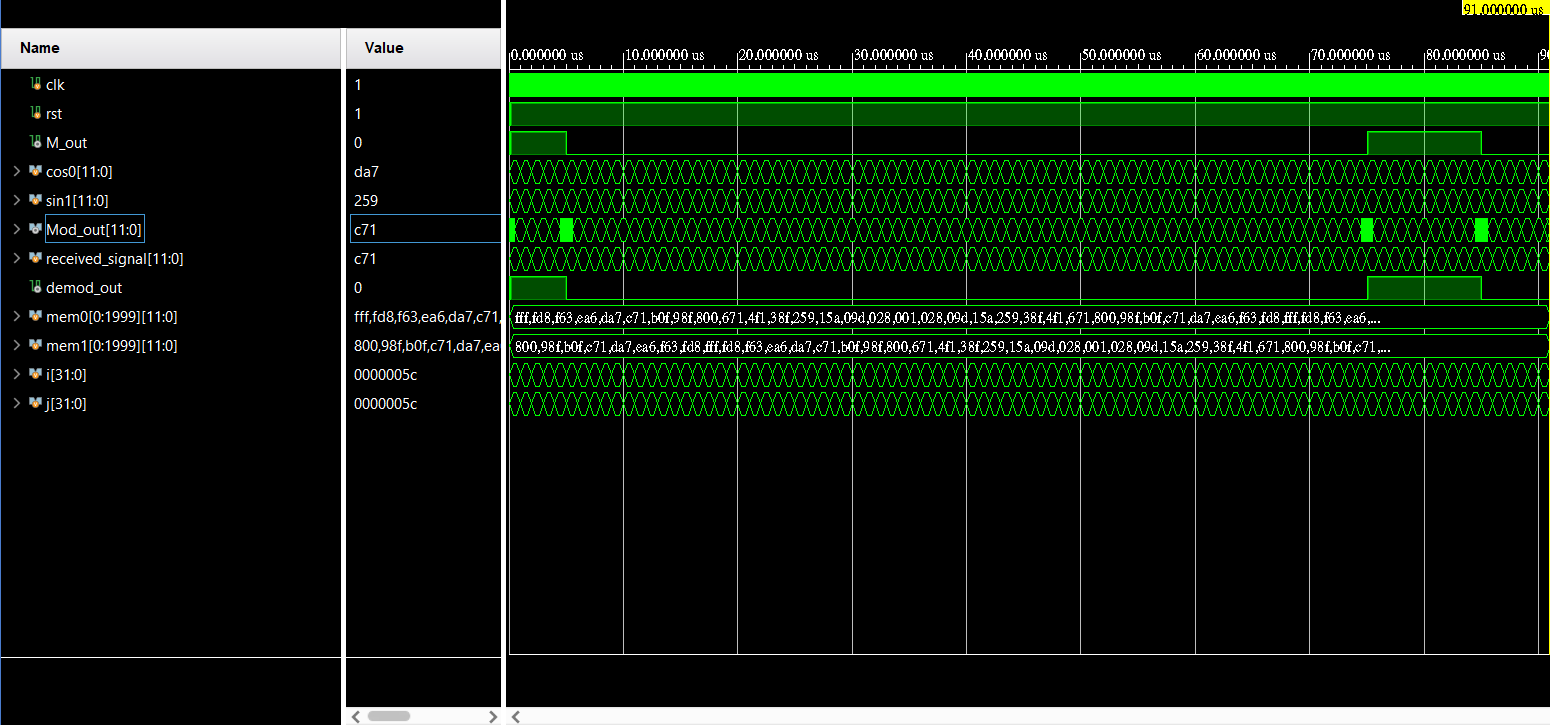
在數位電路設計軟體Vivado 中,輸出模擬圖通常是數位方波圖。
在數位通信中,一些調變方式(如PSK)依賴類比弦波信號作為載波。
因此,能夠在模擬軟體中顯示類比信號是非常重要的。
下方為尚未進行DAC轉換之圖片:
在Vivado中,利用wave style來達成類比訊號的轉換,只需該訊號點擊右鍵,如下圖: